Many Web applications use an architecture called the three-tier architecture, which adds an intermediate layer between the client and the database server
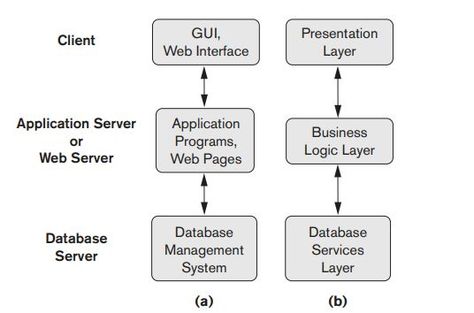
This intermediate layer or middle tier is called the application server or the Web server, depending on the application. This server plays an intermediary role by running application programs and storing business rules (procedures or constraints) that are used to access data from the database server. It can also improve database security by checking a client’s credentials before forwarding a request to the database server. Clients contain user interfaces and Web browsers. The intermediate server accepts requests from the client, processes the request and sends database queries and commands to the database server, and then acts as a conduit for passing (partially) processed data from the database server to the clients, where it may be processed further and filtered to be presented to the users
