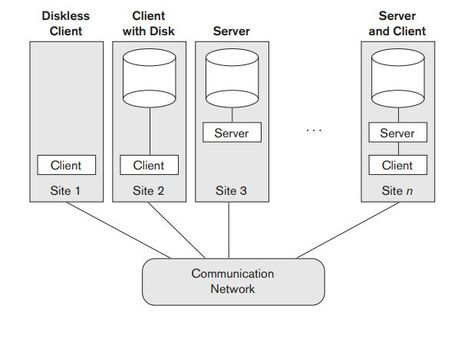
The client/server architecture was developed to deal with computing environments in which a large number of PCs, workstations, file servers, printers, database servers, Web servers, e-mail servers, and other software and equipment are connected via a network. The idea is to define specialized servers with specific functionalities. For example, it is possible to connect a number of PCs or small workstations as clients to a file server that maintains the files of the client machines. Another machine can be designated as a printer server by being connected to various printers; all print requests by the clients are forwarded to this machine. Web servers or e-mail servers also fall into the specialized server category. The resources provided by specialized servers can be accessed by many client machines. The client machines provide the user with the appropriate interfaces to utilize these servers, as well as with local processing power to run local applications. This concept can be carried over to other software packages, with specialized programs—such as a CAD (computer-aided design) package—being stored on specific server machines and being made accessible to multiple clients
The concept of client/server architecture assumes an underlying framework that consists of many PCs/workstations and mobile devices as well as a smaller number of server machines, connected via wireless networks or LANs and other types of computer networks. A client in this framework is typically a user machine that provides user interface capabilities and local processing. When a client requires access to additional functionality—such as database access—that does not exist at the client, it connects to a server that provides the needed functionality. A server is a system containing both hardware and software that can provide services to the client machines, such as file access, printing, archiving, or database access. In general, some machines install only client software, others only server software, and still others may include both client and server software