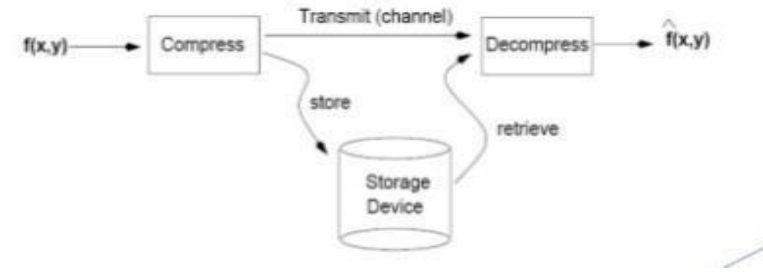
Definition: Image compression deals with reducing the amount of data required to represent a digital image by removing of redundant data.
Images can be represented in digital format in many ways. Encoding the contents of a 2-D image in a raw bitmap (raster) format is usually not economical and may result in very large files. Since raw image representations usually require a large amount of storage space (and proportionally long transmission times in the case of file uploads/ downloads), most image file formats employ some type of compression.
The need to save storage space and shorten transmission time, as well as the human visual system tolerance to a modest amount of loss, have been the driving factors behind image compression techniques
Goal of image compression:
The goal of image compression is to reduce the amount of data required to represent a digital image.
Data ≠ Information:
- Data and information are not synonymous terms!
- Data is the means by which information is conveyed.
- Data compression aims to reduce the amount of data required to represent a given quality of information while preserving as much information as possible.
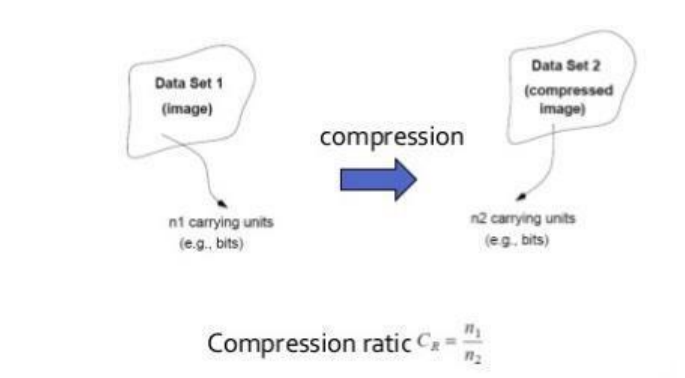
Definition of compression ratio:
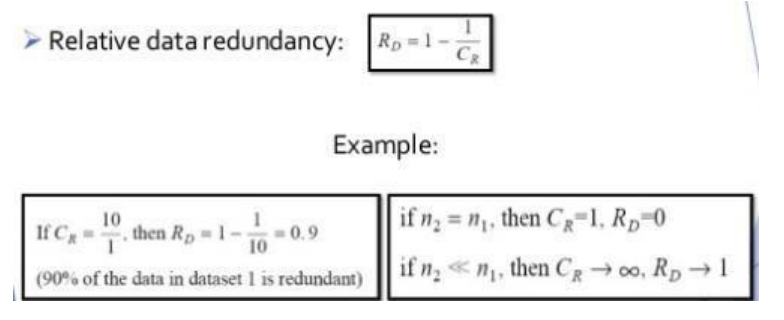
Definitions of Data Redundancy:
Coding redundancy:
- Code: a list of symbols (letters, numbers, bits etc.,)
- Code word: a sequence of symbol used to represent a piece of information or an event (e.g., gray levels).
- Code word length: number of symbols in each code word.
