The union of two sets A and B is the set C which consists of all those elements which are either in A or in B (including those which are in both). In symbols, we write.
A ∪ B = { x : x ∈A or x ∈B }
Venn diagram of Union
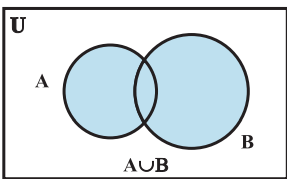
Some Properties of the Operation of Union
- A ∪ B = B ∪ A (Commutative law)
- ( A ∪ B ) ∪ C = A ∪ ( B ∪ C) (Associative law )
- A ∪ φ = A (Law of identity element, φ is the identity of ∪)
- A ∪ A = A (Idempotent law)
- U ∪ A = U (Law of U)
Example of Union in set
Example Let A = { a, e, i, o, u } and B = { a, i, u }. Show that A ∪ B = A
Solution We have, A ∪ B = { a, e, i, o, u } = A.
This example illustrates that union of sets A and its subset B is the set A
itself, i.e., if B ⊂ A, then A ∪ B = A
