Data
Data represents a single value or a set of values assigned to entities. Data item refers a single or group of values with in the data
Entity
An entity is a thing that has some properties which can take values
Information
Processed or meaning full data is called information. This is used for taking some action
Primitive data types
- These are the data structures which are directly supported by the machine. i.e. Any operation can be performed in these data items
- The different primitive data types are
- Integer
- Float
- Double
- Character
- boolean
Non Primitive data types
- These Data structures do not allow any specific instructions to be performed on the Data items directly
- The different non primitive data types are
- Arrays
- Structures
- Unions
- Class etc.
Data structure
- A data structure is an arrangement of data in a computer’s memory or even disk storage. An example of several common data structures are arrays, linked lists, queues, stacks, binary trees, and hash tables
- Algorithms, on the other hand, are used to manipulate the data contained in these data structures as in searching and sorting. Many algorithms apply directly to a specific data structures
- When working with certain data structures you need to know how to insert new data, search for a specified item, and deleting a specific item
- Commonly used algorithms include are useful for:
- Searching for a particular data item (or record).
- Sorting the data. There are many ways to sort data. Simple sorting, Advanced sorting
- Iterating through all the items in a data structure. (Visiting each item in turn so as to display it or perform some other action on these items)
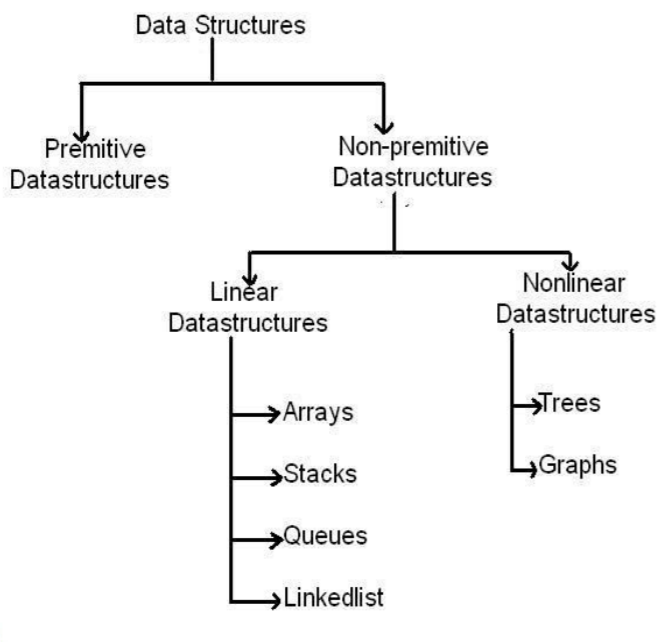
Classification
- There are two types of data structure. They are
- Linear Data structures
- Non-Linear Data structures
Linear Data structures
- This Data Structures involve arranging the elements in Linear fashion.
- Eg.
- Stacks
- Queue
- Lists
Non-Linear Data structures
- This Data structures involve representing the elements in Hierarchical order.
- Eg:
- Trees
- Graphs
Data structure operations
- Operation means processing the data in the data structure. The following are some important operations.
- Traversing
- Searching
- Inserting
- Deleting
- Sorting
- Merging
operations
- Traversing
- To visit or process each data exactly once in the data structure
- Searching
- To search for a particular value in the data structure for the given key value
- Inserting
- To add a new value to the data structure
operations
- Deleting
- To remove a value from the data structure
- Sorting
- To arrange the values in the data structure in a particular order.
- Merging
- To join two same type of data structure values
