The most widely known form of best-first search is called A* search (pronounced “A-star SEARCH search”). It evaluates nodes by combining g(n), the cost to reach the node, and h(n), the cost to get from the node to the goal
f(n) = g(n) + h(n)
Since g(n) gives the path cost from the start node to node n, and h(n) is the estimated cost of the cheapest path from n to the goal, we have
f(n) = estimated cost of the cheapest solution through n
Thus, if we are trying to find the cheapest solution, a reasonable thing to try first is the node with the lowest value of g(n) + h(n). It turns out that this strategy is more than just reasonable: provided that the heuristic function h(n) satisfies certain conditions, A∗ search is both complete and optimal. The algorithm is identical to UNIFORM-COST-SEARCH except that A* uses g + h instead of g
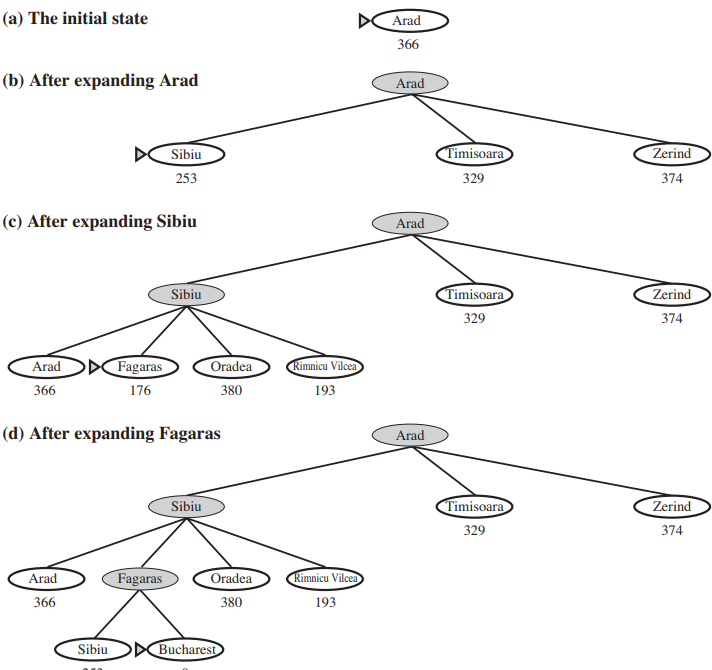
A-star search implementation using java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
/**
* A Star - Heuristic Search Algorithm for finding the shortest path
* Worst Case => O(|E|)
* @author Praneeth
*/
public class AStar {
private PriorityQueue<Node> openList;
private ArrayList<Node> closedList;
HashMap<Node, Integer> gVals;
HashMap<Node, Integer> fVals;
private int initialCapacity = 100;
private int distanceBetweenNodes = 1;
public AStar() {
gVals = new HashMap<Node, Integer>();
fVals = new HashMap<Node, Integer>();
openList = new PriorityQueue<Node>(initialCapacity, new fCompare());
closedList = new ArrayList<Node>();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node[] n = new Node[10];
for (int i = 0; i < n.length; i++) {
n[i] = new Node();
n[i].setData("n-" + i);
}
/*
* X = Walls
* N1 => Start
* N8 => Goal
*
N0 - N3 - N5 - N8
| |
N1 X N6 X
| |
N2 - N4 - N7 - N9
*/
n[0].setXY(0, 0);
n[1].setXY(0, 1);
n[2].setXY(0, 2);
n[3].setXY(1, 0);
n[4].setXY(1, 2);
n[5].setXY(2, 0);
n[6].setXY(2, 1);
n[7].setXY(2, 2);
n[8].setXY(3, 0);
n[9].setXY(3, 2);
n[0].addNeighbors(n[1], n[3]);
n[1].addNeighbors(n[0], n[2]);
n[2].addNeighbors(n[1], n[4]);
n[3].addNeighbors(n[0], n[5]);
n[4].addNeighbors(n[2], n[7]);
n[5].addNeighbors(n[3], n[8]);
n[6].addNeighbors(n[7], n[5]);
n[7].addNeighbors(n[4], n[9], n[6]);
n[8].addNeighbors(n[5]);
n[9].addNeighbor(n[7]);
new AStar().traverse(n[1], n[8]);
}
public void traverse(Node start, Node end) {
openList.clear();
closedList.clear();
gVals.put(start, 0);
openList.add(start);
while (!openList.isEmpty()) {
Node current = openList.element();
if (current.equals(end)) {
System.out.println("Goal Reached");
printPath(current);
return;
}
closedList.add(openList.poll());
ArrayList<Node> neighbors = current.getNeighbors();
for (Node neighbor : neighbors) {
int gScore = gVals.get(current) + distanceBetweenNodes;
int fScore = gScore + h(neighbor, current);
if (closedList.contains(neighbor)) {
if (gVals.get(neighbor) == null) {
gVals.put(neighbor, gScore);
}
if (fVals.get(neighbor) == null) {
fVals.put(neighbor, fScore);
}
if (fScore >= fVals.get(neighbor)) {
continue;
}
}
if (!openList.contains(neighbor) || fScore < fVals.get(neighbor)) {
neighbor.setParent(current);
gVals.put(neighbor, gScore);
fVals.put(neighbor, fScore);
if (!openList.contains(neighbor)) {
openList.add(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
System.out.println("FAIL");
}
private int h(Node node, Node goal) {
int x = node.getX() - goal.getX();
int y = node.getY() - goal.getY();
return x * x + y * y;
}
private void printPath(Node node) {
System.out.println(node.getData());
while (node.getParent() != null) {
node = node.getParent();
System.out.println(node.getData());
}
}
class fCompare implements Comparator<Node> {
public int compare(Node o1, Node o2) {
if (fVals.get(o1) < fVals.get(o2)) {
return -1;
} else if (fVals.get(o1) > fVals.get(o2)) {
return 1;
} else {
return 1;
}
}
}
}
class Node {
private Node parent;
private ArrayList<Node> neighbors;
private int x;
private int y;
private Object data;
public Node() {
neighbors = new ArrayList<Node>();
data = new Object();
}
public Node(int x, int y) {
this();
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public Node(Node parent) {
this();
this.parent = parent;
}
public Node(Node parent, int x, int y) {
this();
this.parent = parent;
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public ArrayList<Node> getNeighbors() {
return neighbors;
}
public void setNeighbors(ArrayList<Node> neighbors) {
this.neighbors = neighbors;
}
public void addNeighbor(Node node) {
this.neighbors.add(node);
}
public void addNeighbors(Node... node) {
this.neighbors.addAll(Arrays.asList(node));
}
public Node getParent() {
return parent;
}
public void setParent(Node parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
public void setXY(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public Object getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(Object data) {
this.data = data;
}
public boolean equals(Node n) {
return this.x == n.x && this.y == n.y;
}
}
