The two dimensional array is also called a matrix.in two dimensional array elements are stored by rows, so the rightmost subscript, or column, varies fastest as elements are accessed in storage order
Here is a sample program that stores roll number and marks obtained by a student side by side in a matrix
main( )
{
int stud[4][2] ;
int i, j ;
for ( i = 0 ; i <= 3 ; i++ )
{
printf ( "\n Enter roll no. and marks" ) ;
scanf ( "%d %d", &stud[i][0], &stud[i][1] ) ;
}
for ( i = 0 ; i <= 3 ; i++ )
printf ( "\n%d %d", stud[i][0], stud[i][1] ) ;
}
The complete array arrangement is shown below
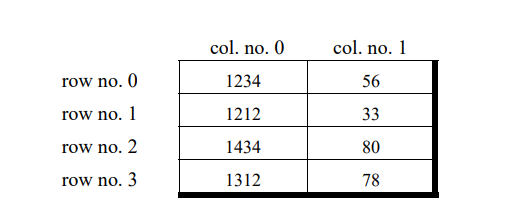
Initialising a 2-Dimensional Array
int stud[4][2] = {
{ 1234, 56 },
{ 1212, 33 },
{ 1434, 80 },
{ 1312, 78 }
} ;
It is important to remember that while initializing a 2-D array it is necessary to mention the second (column) dimension, whereas the first dimension (row) is optional
int arr[2][3] = { 12, 34, 23, 45, 56, 45 } ;
int arr[ ][3] = { 12, 34, 23, 45, 56, 45 } ;
