A pointer is a variable that contains the address of a variable. Pointers are much used in C, partly because they are sometimes the only way to express a computation, and partly because they usually lead to more compact and efficient code than can be obtained in other ways
Pointer Notation
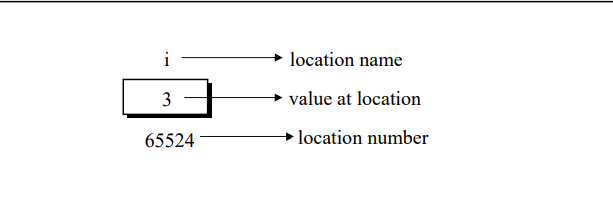
Consider the declaration
int i = 3 ;
This declaration tells the C compiler to:
- Reserve space in memory to hold the integer value.
- Associate the name i with this memory location.
- Store the value 3 at this location.
We may represent i’s location in memory by the following memory map
We can print this address number through the following program:
main( )
{
int i = 3 ;
printf ( “\nAddress of i = %u”, &i ) ;
printf ( “\nValue of i = %d”, i ) ;
}
The output of the above program would be:
Address of i = 65524
Value of i = 3
Look at the first printf( ) statement carefully. ‘&’ used in this statement is C’s ‘address of’ operator. The expression &i returns the address of the variable i, which in this case happens to be 65524. Since 65524 represents an address, there is no question of a sign being associated with it. Hence it is printed out using %u, which is a format specifier for printing an unsigned integer. We have been using the ‘&’ operator all the time in the scanf( ) statement
The other pointer operator available in C is ‘*’, called ‘value at address’ operator. It gives the value stored at a particular address. The ‘value at address’ operator is also called ‘indirection’ operator.
Observe carefully the output of the following program:
main( )
{
int i = 3 ;
printf ( “\nAddress of i = %u”, &i ) ;
printf ( “\nValue of i = %d”, i ) ;
printf ( “\nValue of i = %d”, *( &i ) ) ;
}
The output of the above program would be:
Address of i = 65524
Value of i = 3
Value of i = 3
Note that printing the value of *( &i ) is same as printing the value of i
The expression &i gives the address of the variable i. This address can be collected in a variable, by saying
j = &i ;
But remember that j is not an ordinary variable like any other integer variable. It is a variable that contains the address of other variable (i in this case). Since j is a variable the compiler must provide it space in the memory. Once again, the following memory map would illustrate the contents of i and j

As you can see, i’s value is 3 and j’s value is i’s address.
we can’t use j in a program without declaring it. And since j is a variable that contains the address of i, it is declared as
int *j ;
This declaration tells the compiler that j will be used to store the address of an integer value. In other words j points to an integer. How do we justify the usage of * in the declaration,
int *j ;
Let us go by the meaning of *. It stands for ‘value at address’. Thus, int *j would mean, the value at the address contained in j is an int.
Example
main( )
{
int i = 3 ;
int *j ;
j = &i ;
printf ( "\nAddress of i = %u", &i ) ;
printf ( "\nAddress of i = %u", j ) ;
printf ( "\nAddress of j = %u", &j ) ;
printf ( "\nValue of j = %u", j ) ;
printf ( "\nValue of i = %d", i ) ;
printf ( "\nValue of i = %d", *( &i ) ) ;
printf ( "\nValue of i = %d", *j ) ;
}
Address of i = 65524
Address of i = 65524
Address of j = 65522
Value of j = 65524
Value of i = 3
Value of i = 3
Value of i = 3
