Search engine optimization (SEO) refers to techniques that help your website rank higher in organic (or “natural”) search results, thus making your website more visible to people who are looking for your product or service via search engines
SEO is part of the broader topic of Search Engine Marketing (SEM), a term used to describe all marketing strategies for search. SEM entails both organic and paid search. With paid search, you can pay to list your website on a search engine so that your website shows up when someone types in a specific keyword or phrase. Organic and paid listings both appear on the search engine, but they are displayed in different locations on the page
How Search Engines Work ?
Search engines have one objective – to provide you with the most relevant results possible in relation to your search query. If the search engine is successful in providing you with information that meets your needs, then you are a happy searcher. And happy searchers are more likely to come back to the same search engine time and time again because they are getting the results they need
In order for a search engine to be able to display results when a user types in a query, they need to have an archive of available information to choose from. Every search engine has proprietary methods for gathering and prioritizing website content. Regardless of the specific tactics or methods used, this process is called indexing. Search engines actually attempt to scan the entire online universe and index all the information so they can show it to you when you enter a search query
How do they do it ? Every search engine has what are referred to as bots, or crawlers, that constantly scan the web, indexing websites for content and following links on each webpage to other webpages. If your website has not been indexed, it is impossible for your website to appear in the search results. Unless you are running a shady online business or trying to cheat your way to the top of the search engine results page (SERP), chances are your website has already been indexed.
Big search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo are constantly indexing
hundreds of millions, if not billions, of webpages. How do they know what to
show on the SERP when you enter a search query? The search engines
consider two main areas when determining what your website is about and how
to prioritize it
1:Content on your website:
When indexing pages, the search engine bots scan each page of your website, looking for clues about what topics your website covers and scanning your website‟s back-end code for certain tags, descriptions, and instructions
2:Who’s linking to you:
As the search engine bots scan webpages for indexing, they also look for links from other websites. The more inbound links a website has, the more influence or authority it has. Essentially, every inbound link counts as a vote for that website‟s content. Also, each inbound link holds different weight. For instance, a link from a highly authoritative website like The New York Times (nytimes.com) will give a website a bigger boost than a link from a small blog site. This boost is sometimes referred to as link juice
A few factors that a search engine algorithm may consider when deciding what information to show in the SERP include
- Geographic location of the searcher
- Historical performance of a listing (clicks, bounce rates, etc.)
- Link quality (reciprocal vs. one-way)
- Webpage content (keywords, tags, pictures)
- Back end code or HTML of webpage
- Link type (social media sharing, link from media outlet, blog, etc.)
Before the days of Google (circa 1997), search engines relied solely on indexing web page content and considering factors like keyword density in order to determine what results to put at the top of the SERP. This approach gave way to what are referred to as black-hat SEO tactics, as website engineers began intentionally stuffing their webpages with keywords so they would rank at the top of the search engines, even if their webpages were completely irrelevant to the search result
What it Takes to Rank ?
It is not difficult to get your website to index and even rank on the search engines. However, getting your website to rank for specific keywords can be tricky. There are essentially 3 elements that a search engine considers when determining where to list a website on the SERP: rank, authority, and relevance.
Rank
Rank is the position that your website physically falls in on the SERP when a specific search query is entered. If you are the first website in the organic section of the SERP (don‟t be confused by the paid ads at the very top), then your rank is 1. If your website is in the second position, your rank is 2, and so on. As discussed previously in How Search Engines Work, your rank is an indicator of how relevant and authoritative your website is in the eyes of the search engine, as it relates to the search query entered.
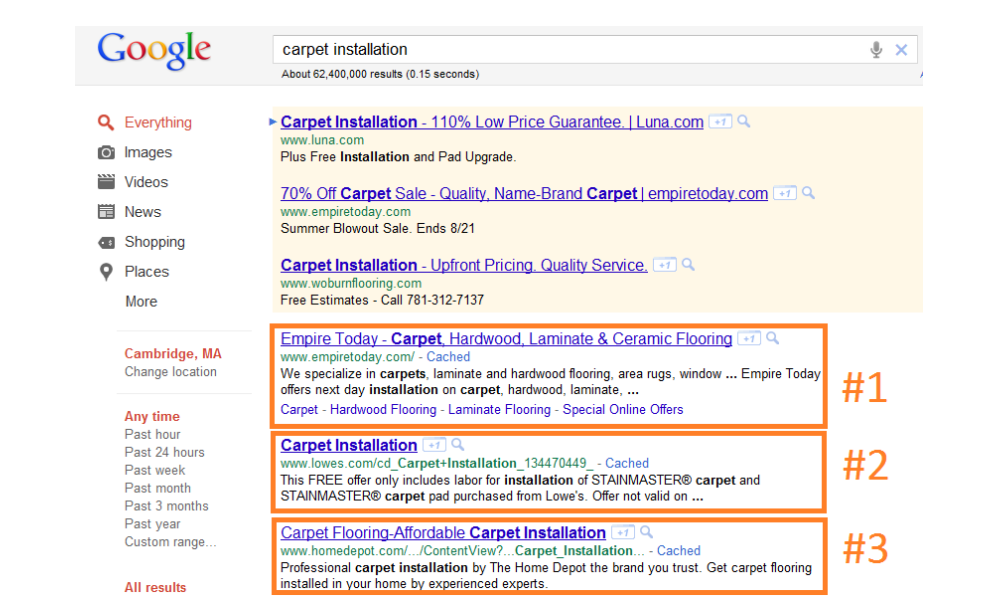
Tracking how your website ranks for a specific keyword over time is a good way to determine if your SEO techniques are having an impact. However, since there are so many other factors beyond your control when it comes to ranking, do not obsess over it. If your website jumps 1-5 spots from time to time, that‟s to be expected. It‟s when you jump 10, 20, 30 spots up in the rankings that it makes sense to pat yourself on the back.
Authority
Search engines determine how authoritative and credible a website‟s content is by calculating how many inbound links (links from other websites) it has. However, the number of inbound links does not necessarily correlate with higher rankings. The search engines also look at how authoritative the websites that link to you are, what anchor text is used to link to your website, and other factors such as the age of your domain
Relevance
Relevance is a one of the most critical factors of SEO. The search engines are not only looking to see that you are using certain keywords, but they are also looking for clues to determine how relevant your content is to a specific search query. Besides actual text on your webpages, the search engines will review your website‟s structure, use of keywords in your URLs, page formatting (such as bolded text), and what keywords are in the headline of the webpage versus those in the body text
Long-Tail Concept & Theory
In order to get your website‟s content to rank on the search engines, you need to take the path of least resistance. Although trying to rank for highly trafficked keywords and terms may seem like a logical approach, it will most likely lead to a lot of frustration and wasted resources. Also, even if you end up getting traffic from these types of keywords, chances are the quality of the traffic will be low due to disinterest in what you specifically have to offer
Think of every search query as being like a snow flake – they are all different. There are billions more unique search queries than there are generic ones. In fact, if you were to add up all search engine traffic that comes from the most popular keywords, it would not even come close to the amount of traffic that comes from searches using those more unique queries. This is called the theory of the long-tail
A critical component of SEO is choosing the right keywords for optimization. If you sell shoes, you may want your website to rank for “shoe store,” (a head term), but chances are you are going to have some trouble there. However, if you optimize multiple pages on your website for each specific pair of shoes that you sell, you are going to have much more success and it will be easier to rank on the SERP. A keyword like “red tennis shoes with Velcro” (a long-tail keyword or term) is a good example. Sure, the number of people that search for this keyword will be much lower than the number that search for “shoe store,” but you can almost bet that those searchers are much farther down the sales funnel and may be ready to buy.
This is why long-tail keywords are so effective. They target people who are looking to perform a specific action, like buy something, or looking for a specific piece of information, like a how-to or a service that can solve their problem. By choosing to optimize with long-tail keywords, you will find it easier to rank on the search engines, drive qualified traffic, and turn that traffic into leads and customers
Content is King
We‟ve all heard it – when it comes to SEO, content is king. Without rich content, you will find it difficult to rank for specific keywords and drive traffic to your website. Additionally, if your content does not provide value or engage users, you will be far less likely to drive leads and customers
It is impossible to predict how people will search for content and exactly what keywords they are going to use. The only way to combat this is to generate content and lots of it. The more content and webpages you publish, the more chances you have at ranking on the search engines. Lottery tickets are a good analogy here. The more lottery tickets you have, the higher the odds are that you will win. Imagine that every webpage you create is a lottery ticket. The more webpages you have, the higher your chances are of ranking in the search engines.
The search engines are smart. If you create multiple webpages about the same exact topic, you are wasting your time. You need to create lots of content that covers lots of topics. There are multiple ways you can use content to expand your online presence and increase your chances of ranking without being repetitive. Here are few examples:
Homepage:
Use your homepage to cover your overall value proposition and high-level messaging. If there was ever a place to optimize for more generic keywords, it is your homepage
Product/Service Pages:
If you offer products and/or services, create a unique webpage for each one of them
Resource Center:
Provide a webpage that offers links to other places on your website that cover education, advice, and tips.
Blog
Blogging is an incredible way to stay current and fresh while making it easy to generate tons of content. Blogging on a regular basis (once per week is ideal) can have a dramatic impact on SEO because every blog post is a new webpage
